In JavaScript, a variable is a symbolic name that represents a value. Variables are used to store and manipulate data within a program. Unlike some other programming languages, JavaScript is dynamically typed, meaning that variables can hold values of any data type, and the data type of a variable can change over time.
Here’s a basic definition of variables in JavaScript:
Declaration: Variables are declared using the var, let, or const keyword, followed by the variable name. For example:
javascript Copy code var x; let y; const z = 10;
Assignment: After declaring a variable, you can assign a value to it using the assignment operator =. For example:
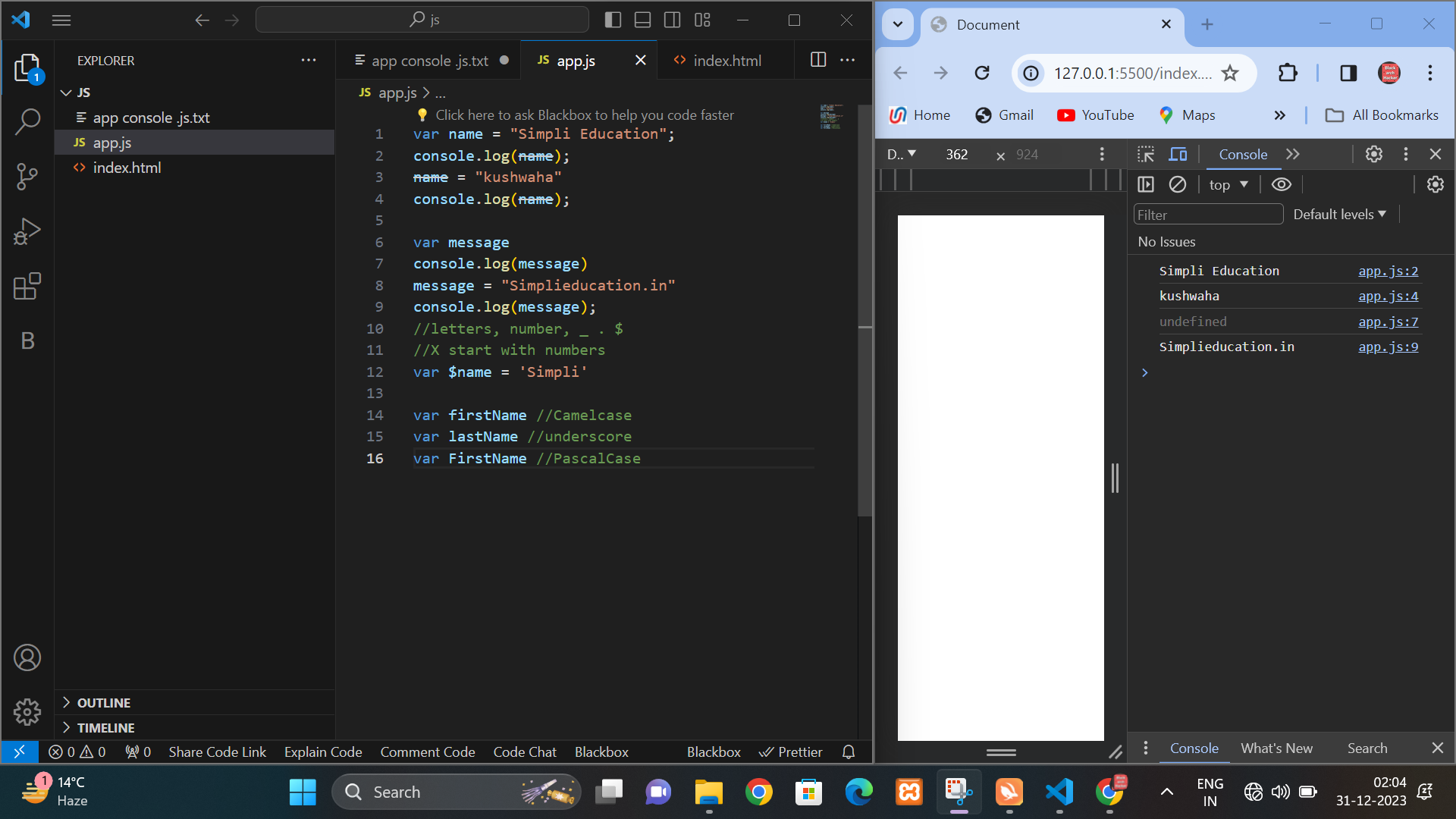
javascript Copy code x = 5; y = "Hello";
Initialization: You can also declare and initialize a variable in a single step. This involves declaring the variable and assigning a value to it simultaneously. For example:
javascript Copy code var a = 10; let b = "World";
Naming: Variable names (identifiers) can consist of letters, digits, underscores, and dollar signs. They must begin with a letter, underscore (_), or dollar sign ($). Variable names are case-sensitive.
javascript Copy code var firstName; var myVariable; var _myVariable; var $myVariable;
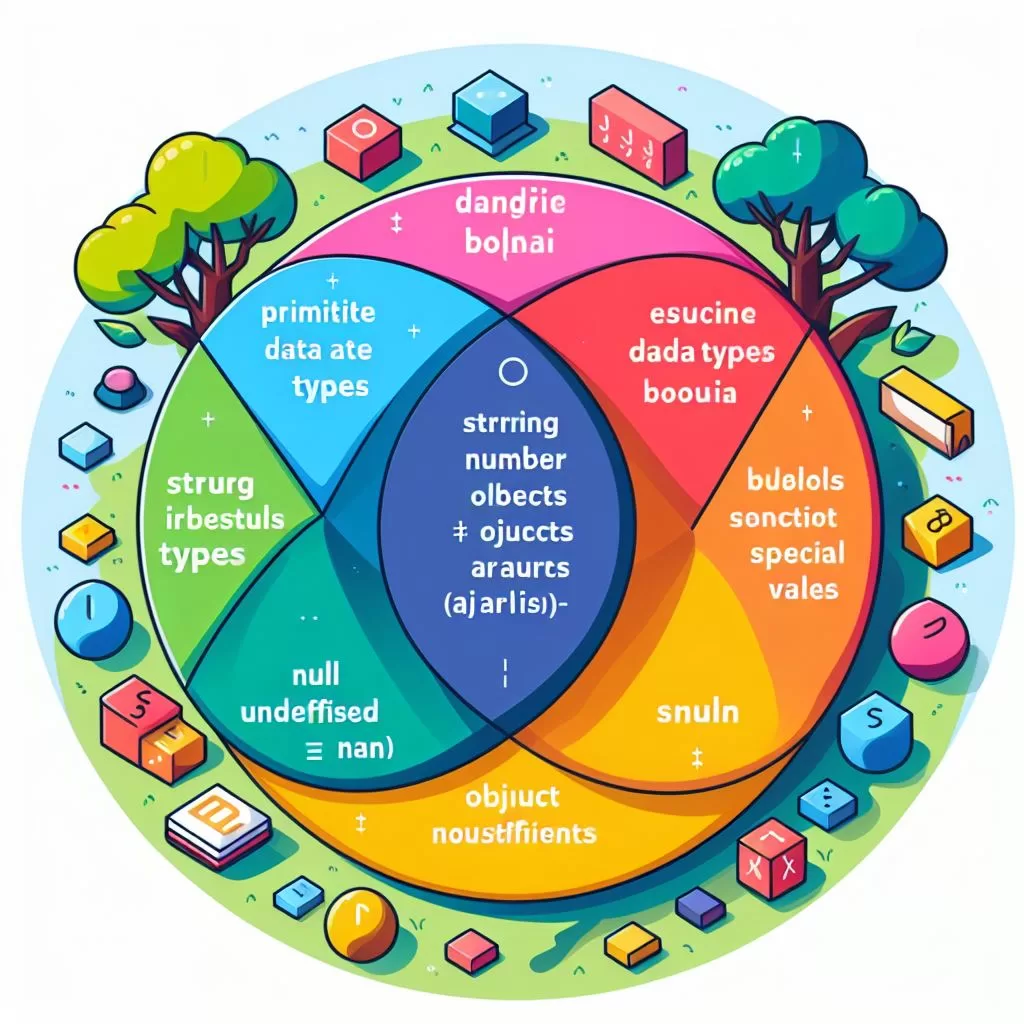
Data Types: JavaScript variables can hold values of various data types, including numbers, strings, booleans, arrays, objects, functions, and more. The data type of a variable is determined dynamically based on the value assigned to it.
JavaScript is a loosely typed language, meaning you don’t need to specify the data type of a variable explicitly. However, you can use the typeof operator to check the data type of a variable at runtime.